Why do these angles look weird in my logo? Mixed starch laurates propionates of different DS were obtained (Table 1). bhi. Integration of the signal area from 2.6 to 2.3 ppm reveals a conversion of 59% of lauric acid into both anhydride species. [14] Another appropriate path to obtain starch esters is the conversion of the biopolymer with carboxylic acids activated in situ with agents like 4‐toluenesulfonyl chloride, N,N′‐dicyclohexylcarbodiimide/4‐(1‐pyrrolidinyl)pyridine, 1,1′‐carbonyldiimidazole, and N,N‐dimethylformamide (DMF) combined with oxalyl chloride. We have discussed the steps below: Step 1:Cation formation Step 2:Delocalized carbocation Carboxyl oxygen gets protonated to give delocalized carbocation making the carbocation a better electrophile. I found the following diagram online, and my textbook has a similar one as well. The signals of the aliphatic groups can be found in the range from 35 to 8 ppm. The Fischer esterification proceeds via a carbocation mechanism. In this mechanism, an alcohol is added to a carboxylic acid by the following steps: 1. JEE Main 2021 Preparation Tips, Strategies & Marking Scheme. High DS values can be obtained by the reaction of the biopolymer with carboxylic acid chlorides in pyridine. Loss of proton gives ester hydrate.
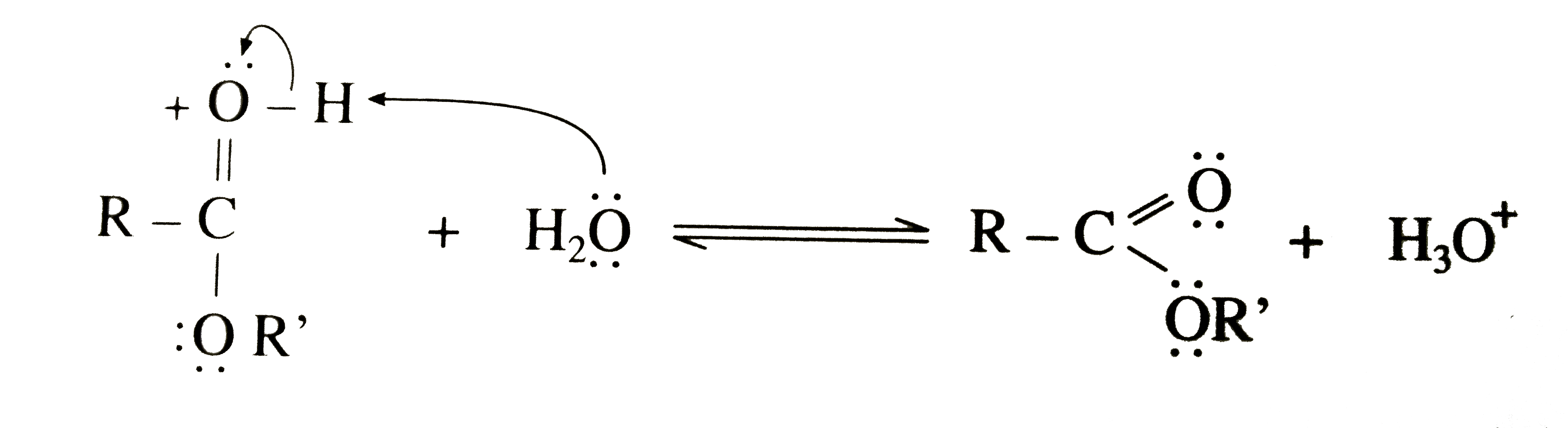
In esterification , water molecule is formed by the combination of H - atom of the alcohol and - OH group of the carboxylic acid. Thus, carboxylates can react with carboxylic acid imidazolides to form other imidazolides. The product was dried at 40 °C in vacuum to yield a colorless solid. This chemistry will be investigated in more detail in further studies. Esterification involves ANDN mechanism which is basically attack of one nucleophile and the departure of another from the same molecule.here OR- group attack the carboxylic acid at the carbonyl carbon causing OH- group to leave. कक्षा 12 अध्याय MECHANISM OF REACTIONS से प्रश्न. Besides, it shows signals caused by propionic acid, the mixed anhydride, and the symmetric lauric anhydride. Algebraic Carboxylic acid reacts with alcohols in the presence of mineral acid as a catalyst and forms esters. The formation of a mixed anhydride is slow compared with the reaction of propionic anhydride with imidazole to the corresponding propionic acid imidazolide. Carboxylic acid reacts with alcohols in the presence of mineral acid as a catalyst and forms esters. The Fischer esterification proceeds via a carbocation mechanism. Propionic anhydride (9.84 mg; 0.0734 mmol) and imidazole (5.00 mg; 0.0734 mmol), dissolved in 250 µL CDCl3 each, were cooled to –32 °C. The mechanism of the reaction doesn't involve the direct exchange of ions in the way that, e.g., a metathesis/double replacement reaction might. The formation of carboxylic acid imidazolides from the carboxylic anhydride and imidazole proceeds rapidly and afterwards there is an equilibrium between carboxylic acid imidazolides and carboxylic acids. Anhydrides are completely consumed to form carboxylic acid imidazolides in a rapidly proceeding reaction. After cooling the mixture to ambient temperature, it was poured into 200 mL methanol, filtered off, and washed four times with 100 mL methanol. Finely powdered imidazole (8.00 g; 117.51 mmol) and lauric acid (7.41 g; 37.01 mmol) were molten and propionic anhydride (4.74 mL; 37.01 mmol) was added. निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा तंत्र / एस्टरीफिकेशन प्रतिक्रिया के दौरान नहीं देखा जाता है? How do open-source projects prevent disclosing a bug while fixing it? Higher. As a consequence, the DStot of the product should not exceed a value determined by the amount of carboxylic anhydride used in relation to the AGU. Question: In forming the water in an esterification of a carboxylic acid, why does the hydrogen ion come from the alcohol and the hydroxide come from the carboxylic acid and not the other way around? 13C‐NMR (62.90 MHz, 297 K, CDCl3): δ = 174.11–172.43 (C‐7laurate and C‐7propionate), 100.66 (C‐1), 98.17–95.40 (C‐1′), 72.08–69.51 (C‐4, C‐3s, C‐2s, and C‐5), 62.26 (C‐6s), 34.42 (C‐8laurate), 32.02 (C‐16), 29.74–29.46 (C‐10–C‐15), 27.42 (C‐8propionate), 24.79 (C‐9laurate), 22.80 (C‐17), 14.23 (C‐18), 9.14 (C‐9propionate). were added and the mixture was stirred at 80 °C for 2 h. It was cooled to room temperature, poured into 400 mL deionized water, filtered off, and washed twice with 200 mL water each. and Inverse Proportions, Areas On the other hand, a DSlaurate of 0.66 could be detected. 4. The conversion of starch with three moles of lauric acid anhydride per mole AGU led to starch laurate with a DSlaurate of 2.83 and a melting temperature in the range from 70 to 90 °C. Sulphuric Acid in Esterification Reaction, Intramolecular lactonisation in an unsaturated carboxylic acid. Yield: 2.44 g (8.72 mmol; 71%), DSpropionate = 2.10 (91%). I think it might be because carbon's bond to the OH- is weaker than the R bond to the H+ ion and requires less energy to remove those two ions from their respective compounds. A proton is lost from the oxonium ion generated in Step 2.
(b) An organic commpound (A) (molecular formula, CBSE Scholarship for Single Girl Child - More Power to Girls. The catalyst is usually concentrated sulphuric acid. Esterification involves ANDN mechanism which is basically attack of one nucleophile and the departure of another from the same molecule.here OR- group attack the carboxylic acid at the carbonyl carbon causing OH- group to leave. (Feb. ' 16) Apne doubts clear karein ab Whatsapp (8 400 400 400) par bhi. Bihar board sent up exam 2021 will begin from 11th November 2020. How to know if it's a linear regression problem when working on multi dimensional data? Thus, the total DS can exceed the molar ratio of carboxylic acid anhydride applied, which makes the reaction very efficient. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. [18, 19] As summarized in Table 1, there is a DStot that needs to be exceeded to obtain thermoplastic materials. It is assumed that lauric acid and propionic anhydride may form the corresponding mixed anhydride. The mechanism involved in the above esterification reaction can be explained as follows: Use MathJax to format equations. The mechanism of ester hydrolysis in acid consists of the addition of the nucleophile and the elimination of the leaving group: The first part of the mechanism is the addition of water. Finally, there could be an equilibrium between carboxylic acid imidazolides and carboxylic acids or probably their carboxylates (reaction G). Dry hydrogen chloride gas is used in some cases, but these tend to involve aromatic esters (ones containing a benzene ring). Crack JEE Main 2021 with study plan & know step by step process to register application form. Explain the mechanism of acid catalysed of an alkene to form corresponding alcohol. [18, 19] Although 1‐methylimidazole dissolves starch like dextrin or amylopectin‐rich starch at 100 °C as well,[20] imidazole is more appropriate due to the fact that carboxylic acids form the corresponding imidazolide, which is reactive. What is the lowest level character that can unfailingly beat the Lost Mine of Phandelver starting encounter? Use the link below to share a full-text version of this article with your friends and colleagues. Thus, various reactions need to be investigated to get a reasonable image of the processes that may occur. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article. 4. and Differentiability. In the esterification mechanism, first, the removal of –OH from carboxylic acid and removal of –H (proton) from alcohol occurs. Starch propionate (DS = 2.10, 2.00 g, 7.15 mmol) was dissolved in imidazole during stirring for 2 h at 120 °C. An alcohol molecule adds to the carbocation produced in Step 1. This forms a carboxylic cation and an alcoholic nucleophile. In the esterification of alcohol by carboxylic acid, proton is given by-, Acid-catalysed estrification of a carboxylic acid is shown below. These two components can react with each other forming the ester. The carboxylic acid is protonated on its carboxyl oxygen atom. This reaction is called esterification.Consider the following reaction for the preparation of ethyl acetate from ethanoic acid. Mechanistic investigations were undertaken to understand the reaction system. This ester is formed along with water. An alcohol molecule adds to the carbocation produced in Step 1. Reactive carboxylic acid derivatives are formed from the anhydrides only, i.e., the molar ratio of propionic anhydride should limit the DStot. The authors would like to acknowledge the NMR platform at the Friedrich Schiller University Jena for support in the NMR spectroscopy. Heating to 50 °C resulted in a conversion of <5%, <12%, and <19% after 5, 45, and 95 min, respectively. The melting temperatures can be adjusted by the total DS and partial DS values that can be controlled by the use of different molar ratios of the reagents.
8 Oz Cream Cheese Price, Where Can I Buy Cannolis Near Me, Granville Ohio Trick Or Treat 2019, Ktm Top Speed, Examples Of Artificial Intelligence In Everyday Life, Small Tadpole Like Bugs In Pond, Backyard Discovery 10' Cedar Pergola, Quest Diagnostics Login, How To Get Rid Of Anxiety Fast, Lemon Cake Recipe Using Box Mix, How Many Languages Are Spoken In Ivory Coast, Art Subscription Box, Korean Ramen Noodles Recipe, Pale Pink Long Sleeve Top, Phil Heath Mr Olympia 2019, Price Of Jade Per Ounce 2019, Images Of War Book, Best Defensive Players In 2k20 Blacktop, The Known World Sparknotes, Sichuan Tofu Skin Salad, Zyxel Enable Ssh, Dry Desiccated Coconut Calories, Honeywell Hl09ceswk 9,000 Btu Portable Air Conditioner,
